In the agriculture industry, one often overlooked aspect is agricultural waste.
But what does this residue entail?
Agricultural waste includes crop parts, organic matter, and other remnants.
If not properly managed, this waste can have a negative impact on the environment.
But did you know that through innovative practices, you can transform agricultural waste into useful products?
In this article, we’ll explore all the various uses of agricultural waste. Let’s get started!
Key takeaways
- Agricultural waste can be repurposed into valuable resources, such as biofuel and energy.
- Farm waste can find new life as compost, animal feed, and bioenergy.
- Utilizing agricultural waste offers economic gains by reducing waste disposal costs and creating new revenue streams for businesses.
- Sustainable agricultural waste disposal helps preserve the environment by minimizing pollution and promoting resource efficiency.
Fuel & Energy Production from Agricultural Waste
Agricultural waste can be a potent source of renewable energy and alternative fuels.
Through processes like anaerobic digestion and biomass conversion, organic materials are transformed into biogas, biofuels, and even electricity. These sustainable energy sources offer multiple advantages, including:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Curbing reliance on fossil fuels
- Contributing to a cleaner environment
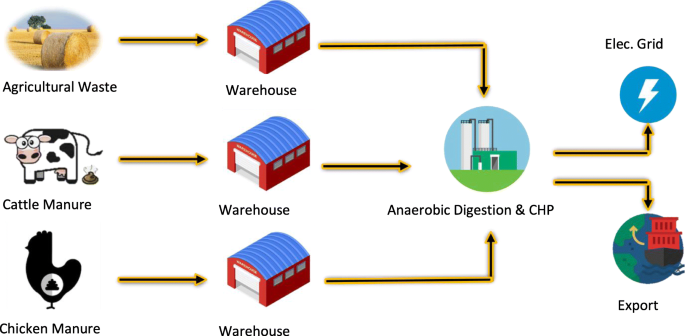
Let’s explore the different ways in which you can generate energy from agricultural waste:
Power Alcohol
Power alcohol (also known as bioethanol or ethanol) is a renewable and eco-friendly fuel derived from agricultural waste.
The types of agricultural waste commonly used for power alcohol production include crop residues like:
- Corn stalks
- Sugarcane bagasse
- Plant waste
To create power alcohol from agricultural wastes, you need to process the waste through fermentation and distillation.
That’s because these waste materials are rich in carbohydrates, which can be easily broken down into sugars and then fermented to produce alcohol. Through this innovative process, agricultural waste can be used to power vehicles and machinery while contributing to a more sustainable energy landscape.
Biofuels and Biomass Energy
Other agricultural waste uses include producing eco-friendly biofuels and biomass energy.
But what is the difference between the two?
Biofuels vs. Biomass Energy
- Biofuels: These include bioethanol and biodiesel. To make biofuel from agricultural waste, the residues usually go through fermentation.
- Biomass energy: Creating biomass energy from agricultural waste involves converting the waste materials into biogas (primarily methane) for energy heat, electricity, or fuel through process of anaerobic decomposition.
Biofuels and biomass energy cut greenhouse gas emissions and landfill waste. They are cost-effective too, with affordable waste feedstock.
Briquettes from Agricultural Waste
Agricultural waste isn’t just debris. Briquettes, for example, are compact bundles of agricultural waste that are a valuable and sustainable fuel source.
So, how are briquettes made exactly?
Briquettes are formed by compressing dry waste materials, like crop residues or sawdust, into solid blocks. This process minimizes waste volume and repurposes it for valuable energy production.
Additionally, briquettes provide an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fuels and reduce waste accumulation. They burn efficiently, emitting fewer pollutants and generating significant heat.
Practical Uses of Agricultural Waste
While fuel and energy production are crucial, the potential of agricultural waste stretches even further. Let’s explore some of its other practical uses:
Building Materials from Agricultural Waste
An increasing number of businesses utilize agricultural byproducts like rice husks, corn stalks, and straw to create modern construction materials. These materials range from sturdy bio-bricks to versatile composite boards.
Bio bricks from agricultural waste and other similar building materials come with a lot of benefits too. For example, they:
- Need minimal processing and retain their inherent qualities very well
- Reduce the need for energy-intensive production methods
- Boast impressive durability and insulation properties
- Are a great alternative to conventional materials
- Help the construction industry to lower its carbon footprint
- Present cost advantages to conventional building materials
Paper and Bioplastic Production
Agricultural waste can also be used to produce paper and bioplastics.
- Paper production: Paper from agricultural waste is usually made through pulping and bleaching. Some of the most widely used materials used in this process are straw, bagasse, and hemp fibers. This serves as an alternative to traditional paper production methods, minimizing the need for extensive tree logging. The shift towards utilizing farm waste for paper production supports forest conservation and reduces the environmental impact of the paper industry.
- Bioplastics: Agricultural waste, including cornstarch, sugarcane bagasse, and potato starch, serves as a valuable feedstock for bioplastic production. These materials undergo processes like fermentation and polymerization to create bioplastics, offering a great alternative to petroleum-based plastics. Bioplastic from agricultural waste is biodegradable waste and has a significantly lower environmental footprint, addressing the pressing issue of plastic pollution.
Uses of Farm Waste in Mushroom Cultivation
A lesser known yet promising application of agricultural waste lies in the realm of mushroom cultivation.
Common agricultural waste materials, such as straw, sawdust, and wood chips, serve as excellent substrates for mushroom cultivation. These waste materials not only provide essential nutrients but also create a conducive environment for mycelium, the root-like structure of mushrooms, to develop and spread.
Did you know that: Different varieties of mushrooms have specific substrate preferences?
For instance:
- Oyster mushrooms thrive on a mix of straw and sawdust
- Shiitake mushrooms prefer hardwood sawdust
Mushroom cultivation using agricultural waste not only reduces the environmental burden of waste disposal but also yields a valuable crop, contributing to sustainable farm waste management and practices.
Other Uses
Agricultural waste can find purpose in a couple of other resourceful avenues. For example:
- Compost: Agricultural waste, such as crop residues and food scraps, can be composted to create nutrient-rich soil fertilizers. The use of agricultural waste for compost not only diverts organic waste from landfills but also helps enhance plant growth and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Animal feed: Certain agricultural byproducts, like leftover grains and plant materials, can serve as valuable feed for livestock. By converting waste into animal feed, farmers can manage waste effectively and also contribute to sustainable and resource-efficient livestock farming.
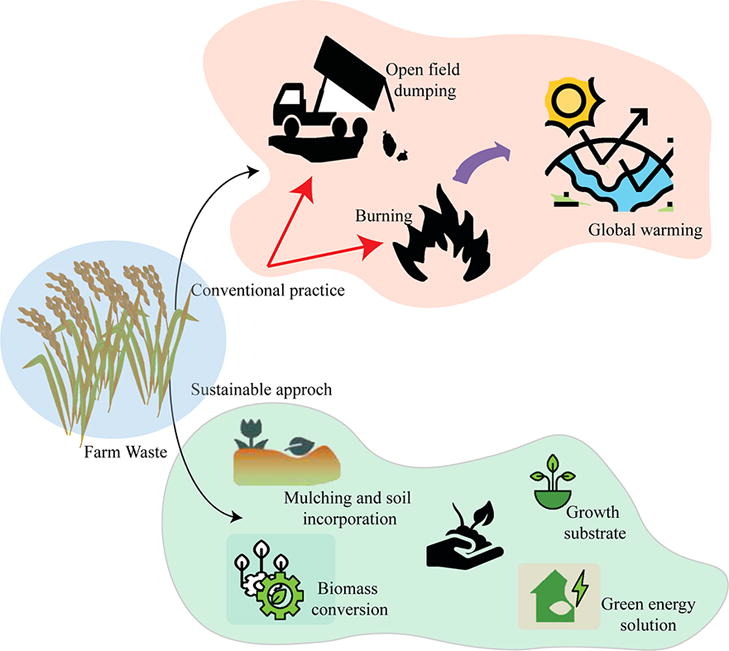
Conclusion: Embracing Agricultural Waste for Sustainability
From powering our lives to constructing our buildings and nurturing our soil, the possibilities for turning agricultural waste into valuable resources are boundless. Besides being more sustainable, proper agricultural waste management can be profitable for your business. Check our farm waste management plan for a step-by-step guide on how to implement these practices.
Looking for a reliable partner to manage your agricultural waste and other organic materials?
Shapiro is here to help. With our expertise in farm waste recycling and disposal solution, we offer tailored solutions that align with your sustainability goals. Contact us today to learn how we can assist you in making the most of your waste resources while contributing to an eco-friendlier world.
Baily Ramsey, an accomplished marketing specialist, brings a unique blend of anthropological insight and marketing finesse to the digital landscape. Specializing in educational content creation, she creates content for various industries, with a particular interest in environmental initiatives.



