Did you know that food waste on farms amounts to 1.2 billion tons per year?
Farm waste is the result of different agricultural activities. If not disposed of properly, this waste can harm the environment and can even affect your bottom line.
To treat farm waste effectively, farmers can use comprehensive farm waste management plans.
But how do you develop an agricultural waste management plan in the first place?
Let’s explore what farm waste management is, all the steps involved in creating a comprehensive waste management plan, and other FAQs.
What is Farm Waste Management?
Farm waste management involves implementing different practices related to handling and disposing of waste generated in agricultural operations.
This waste includes:
- Crop residues
- Animal manure
- Packaging materials
- Agricultural byproducts
Having farm waste management practices in place can help you minimize environmental pollution, enhance soil fertility, and have an overall more sustainable business.
But how do you create a well-designed farm waste management plan?
What is Waste Management Plan: Do I Need it?
A waste management plan outlines the strategies, procedures, and actions a business can implement to effectively manage waste.
In the agriculture industry, a farm waste management plan can help:
- Ensure compliance with environmental regulations and guidelines related to waste disposal
- Encourage waste reduction, reuse, and recycling
- Improve operational efficiency, minimize costs
- Enhance business sustainability
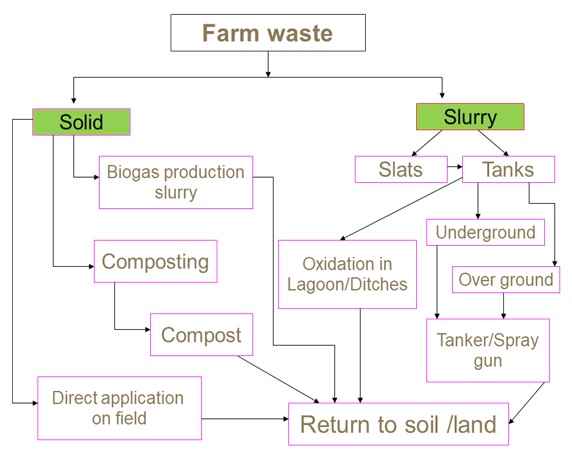
Effective Waste Management Planning in 7 Simple Steps
Creating a comprehensive waste management plan can be overwhelming if you don’t know what components you should take into consideration. One way to approach this is by using a readily available waste management plan template.
But to make things even easier, we created this step-by-step guide you can follow:
Step 1: Identify the Waste Your Facility Creates
At this stage, you need a detailed breakdown of what waste your business generates.
To do that, you can conduct a waste audit that:
- Identifies and categorizes different types of waste
- Measures the quantities of waste produced
- Evaluates your current disposal methods
Conducting a waste audit will help you gain valuable insights into your facility’s waste stream and come up with waste reduction strategies, better resource allocation, and an effective waste management plan.
Step 2: Identify Waste Streams
This step involves categorizing waste streams based on their specific characteristics and identifying all regulations involved in handling them.
For example, it’s important to identify which waste is:
- Hazardous: This type of waste (e.g., biologically contaminated waste) poses potential risks to human health and the environment. That’s why it requires specific handling, storage, and disposal methods that comply with environmental regulations.
- Non-hazardous: This waste causes no harm to human or environmental health. However, if your farm produces large quantities of such waste, you still need to abide by the regulatory considerations associated with it.
Ultimately, identifying the different types of waste can help you implement the right collection, treatment, and recycling methods to optimize your waste management efforts.
Step 3: Establish a Waste Management Team
Having a waste management team is essential as these are the people who will oversee and drive continuous improvement in all waste management practices.
This team will be responsible for:
- Implementing waste reduction strategies
- Ensuring compliance with regulations
- Fostering a culture of sustainability
To ensure a solid team, you need to clearly define each team member’s roles.
For example, having a waste management coordinator can help with overseeing all waste management activities.
Additionally, team members should be assigned specific responsibilities. This ensures accountability and facilitates efficient waste management practices throughout the facility.
Step 4: Assess Current Waste Disposal Methods
Assessing your current waste disposal methods will help you identify inefficiencies, potential risks, and areas of improvement.
You can evaluate specific aspects of your waste disposal system, such as:
- Waste bin placement: Here, you need to assess whether bins are strategically located throughout all facilities. Think: Are they encouraging waste segregation? Do they reduce the chances of waste being improperly disposed of or accumulating in inappropriate areas? Do workers have convenient access to them?
- Labeling: Effective labeling provides clear instructions on proper waste segregation and disposal. Ensure your waste bins and containers are labeled appropriately with clear signage and instructions.
- Reliability of waste pickup services: This involves evaluating the consistency of waste collection. Efficient pickup services can prevent waste accumulation, maintain cleanliness, and ensure that waste is disposed of according to regulations and environmental standards.
Step 5: Consider Your Waste Hierarchy
You can use the waste hierarchy framework when making waste management decisions at each of the following levels:
- Waste reduction: This is the highest level in the hierarchy. It involves minimizing waste generation at its source and can be achieved through efficient production processes, optimized inventory management, and sustainable packaging solutions.
- Reuse: At this level, you can find alternative uses for products, equipment, or materials, extending their lifespan and reducing the need for new resources. Think: refurbishing machinery, repurposing containers, or donating surplus food.
- Recycle: Recycling involves converting waste into new products or raw materials. It involves collecting and processing recyclable materials (such as paper, plastics, glass, or metal) and transforming them into new items. To do that, you can implement recycling programs that ensure proper segregation and collection of recyclable materials.
- Recovery: The aim here is to extract energy or other resources (that otherwise cannot be recycled) from waste. This includes practices such as anaerobic digestion (converting organic waste to biogas) and waste-to-energy systems that convert waste into electricity or heat.
- Responsible disposal: Your waste cannot be reduced, reused, recycled, or recovered? That’s where responsible disposal comes in. It involves disposing of waste in an environmentally sound manner, adhering to all regulations and guidelines (such as using approved landfill facilities or incineration methods).
Implementing strategies at each level of the hierarchy can help optimize your overall resource utilization and benefit your bottom line.
Step 6: Select the Right Waste Management Partner
Do all the steps so far sound too overwhelming? We get it!
Going through an extensive audit, evaluating all your waste streams, identifying your main disposal methods, and understanding your shortcomings can be challenging. Additionally, following a simplified waste management template might not work for you, especially if you have more complex operations and your business is spread across different locations and facilities.
That’s why many companies opt for partnering with a waste management expert that will do all the heavy lifting for them.
When selecting agricultural waste management service, you should:
- Look for waste management companies with extensive experience in agricultural waste disposal.
- Ensure that the waste management partner offers a range of services that align with your farm’s specific needs.
- Verify that the company follows strict environmental regulations and possesses the necessary permits and certifications.
- Understand whether they leverage advanced technologies to optimize waste management processes.
At Shapiro, we have 30 years of experience in providing agricultural recycling services. We take care of farm waste in the most responsible way possible, no matter what facility or operation you have. You can rest assured that we do all that in compliance with relevant health and safety regulations.
Step 7: Set Targets for Waste Reduction
Establishing specific goals can enable you to track progress and drive continuous improvement in waste management practices. Here are a few pointers to keep in mind:
- Focus and accountability: Having clear goals means your team can work towards specific targets. This can significantly increase the adoption of sustainable waste management practices in your everyday operation.
- Measuring progress: Setting goals allows you to track progress on your waste reduction efforts. For example, you can track waste volume, recycling rates, or diversion rates.
- Identifying areas for improvement: Having specific goals helps identify where waste reduction initiatives can be implemented. For instance, you could aim to reduce food waste in harvesting processes, implement composting programs, or minimize packaging waste.
- Continuous improvement: As waste reduction is an iterative process, you should constantly set new targets to push for even greater waste reduction. This allows your farm to continuously improve in this area and strive for higher levels of sustainability.
Some specific goals you can set for your farm are:
- Reduce food waste by 15% within the next year through improved inventory management.
- Increase recycling rates by 10% by using recycled packaging materials and biodegradable plastics.
- Minimize water waste by half through efficient irrigation practices.
Goals and Objectives of Farm Waste Management Plan
Having a farm waste management plan targets a few specific goals and objectives:
Environmental Sustainability
An effective farm waste management plan can minimize the release of harmful substances into the environment and protect ecosystems and natural resources. This can help farms contribute to a greener and more sustainable agricultural sector.
Operational Efficiency
If you have a solid plan in place, you can also streamline waste handling processes, minimizing the time spent on waste management activities. This allows farmers to focus on other important activities and maximize productivity.
Compliance with Legal Requirements
Aligning your waste management plan with legal and regulatory requirements ensures that the farm operates in accordance with all regulations. This is crucial if you want to avoid hefty fines or legal penalties.
Enhanced Farm Productivity and Profitability
With 15% of food wasted at a farm level, you can imagine the losses many farmers have to face. By reducing waste generation, your farm can minimize losses and maximize resource efficiency, increasing your overall productivity and profitability.
Farm Waste Management Plan
Farm waste management plans include a few elements:
Waste Identification and Assessment
Identification and assessment of waste involves:
- Categorizing waste into different groups: These could be organic waste, packaging materials, agricultural byproducts, etc.
- Assessing the volume of each waste type: This allows you to gain valuable insights into how much waste you generate and how it impacts the environment and your business.
- Identify areas for improvement: Once you identify relevant improvement areas, you can implement targeted waste reduction strategies and disposal methods to minimize environmental harm.
Waste Minimization and Source Reduction
Your farm waste management plan should aim to minimize waste generation at the source. For example, you can explore opportunities for process optimization to reduce the overall amount of waste produced.
By improving production practices and implementing recycling initiatives, you can significantly reduce your farm’s environmental footprint. This can be further optimized by educating and training your personnel on waste reduction techniques and best practices. This ensures that everyone on site is working towards sustainable farming practices.
Waste Handling and Storage
Even when you reduce waste to a minimum, you can’t bring it down to zero. But what you can do is know how to store it properly, so it has no negative impact on the environment or your bottom line.
For example, you need to ensure to segregate your waste properly to prevent environmental pollution and cross-contamination. You can do that by:
- Using appropriate containers, bins, or special waste storage facilities
- Implementing measures to prevent leaks, spills, or contamination during storage
Waste Recycling and Reuse
Identifying recycling and reuse opportunities can help you reduce your waste and its environmental impact.
For example, you can explore options for anaerobic digestion or composting your organic waste. This way, you can produce biogas or compost that can be used at your farm. The result? Such innovative strategies are not only environment-friendly but also help you maximize resource efficiency.
Waste Treatment and Disposal
Another crucial element of an effective farm waste management plan is the proper treatment and disposal of waste.
This involves:
- Determining suitable treatment methods for specific waste types
- Taking into account the waste composition and potential environmental impacts.
- Ensuring compliance with local regulations regarding waste disposal
- Exploring the possibilities of partnerships with waste treatment or disposal facilities. Such establishments provide access to specialized expertise and infrastructure when handling certain waste streams.
Monitoring and Record-Keeping
Implementing a comprehensive monitoring and record-keeping system allows you to:
- Track and monitor waste generation, handling, and disposal practices
- Ensure compliance with the established waste management plan
- Maintain detailed records of waste quantities and disposal methods
- Evaluate your waste management efforts and identify areas for improvement
Regularly reviewing and evaluating the plan’s effectiveness ensures continuous refinement and more informed decision-making.
Training and Education
Comprehensive training and education to farm personnel can go a long way. Through training programs, farm workers can:
- Gain the needed knowledge and skills to implement proper waste management practices
- Promote awareness of the importance of waste management
- Actively participate in waste reduction practices
- Be always updated on any changes to waste management regulations, ensuring compliance
Continuous Improvement and Review
A farm waste management plan is not a static document but rather a dynamic process. That’s why it requires continuous improvement and review.
Regular assessments of the plan’s effectiveness are crucial for ongoing success. You can seek feedback from employees, stakeholders, or waste management professionals to make any necessary adjustments and updates to the plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Got any other questions about waste management plans? Here are the answers to some commonly asked questions:
What Should a Good Waste Management Plan Include?
A good waste management plan should include:
- A comprehensive assessment of waste types
- An evaluation of current waste disposal methods
- Clear waste reduction goals
- Well-defined strategies for waste reduction and recycling
- Proper waste handling and disposal methods
- Monitoring and record-keeping procedures
- A framework for continuous improvement
What are the Objectives of Waste Management?
Waste management aims to:
- Minimize waste generation
- Promote proper waste handling and disposal practices
- Reduce environmental pollution
- Conserve resources
- Protect public health
- Comply with waste management regulations
- Promote sustainability by maximizing the reuse, recycling, and recovery of waste materials
- Achieve a circular economy
How do you Create a Waste Management Plan?
To create a waste management plan, you should:
- Conduct a thorough waste audit
- Set achievable goals
- Assemble a waste management team
- Develop strategies to minimize waste generation
- Implement proper waste disposal methods
- Establish monitoring systems
- Regularly review and update the plan as needed
What Types of Waste are Typically Generated on a Farm?
Typical waste generated on a farm includes:
- Organic waste: Crop residues, spoiled produce, and animal manure
- Non-organic waste: Packaging materials, plastic waste, and hazardous materials (such as pesticides or chemicals)
How Can a Farm Waste Management Plan Improve Sustainability in Agriculture?
A farm waste management plan can improve sustainability in agriculture by
- Reducing waste sent to landfill
- Minimizing environmental pollution
- Conserving resources through recycling and composting
- Promoting responsible waste handling practices
- Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations
How Can Composting be Integrated into a Farm Waste Management Plan?
Composting can be integrated into a farm waste management plan by collecting organic waste materials, which can be processed to produce nutrient-rich compost. This compost can be re-integrated into the farm’s operations as organic fertilizer for crops.
Can a Farm Waste Management Plan Help to Save Costs?
Yes, a farm waste management plan can help save costs by:
- Reducing waste disposal expenses
- Improving operational efficiency
- Optimizing resource utilization
- Minimizing the need for external waste management services
- Generating value from recycled materials or compost that can be used on the farm
Baily Ramsey, an accomplished marketing specialist, brings a unique blend of anthropological insight and marketing finesse to the digital landscape. Specializing in educational content creation, she creates content for various industries, with a particular interest in environmental initiatives.



