Dairy farming is fundamental to the global food industry and provides consumers with a large selection of products like milk, yogurt, cheese, and much more. However, with such a variety of dairy products available, unfortunately a significant amount of dairy waste is produced, which can pose environmental and health risks if not managed properly. In fact, according to a survey conducted by Edinburgh University for The Guardian, around 16% of dairy products (equivalent to 116 million tons) are lost or wasted annually, making it essential to implement effective dairy waste management strategies.
In this article, we will explore the importance of dairy waste management, the sources and characteristics of dairy waste, how to properly handle it, treatment processes, laws around dairy waste management, and more.
Key Takeaways
- Dairy waste includes a wide range of substances like excess milk from spills, cleaning solutions, whey, residues from equipment, and other organic matter.
- If not managed or treated properly, dairy waste can lead to water and environmental contamination.
- Dairy waste is composed of a large percentage of organic matter that is typically broken down by microorganisms.
- By adhering to the federal laws and regulations and collaborating with waste management experts, you can ensure your dairy waste is handled safely and properly.
What is Dairy Waste?
The dairy industry generates dairy waste during the production, processing, and distribution of dairy products. Sources of dairy waste include a wide range of substances like excess milk from spills, cleaning solutions, whey, residues from equipment, and other organic matter. These wastes can contaminate water sources, contribute to air pollution, and harm ecosystems. By putting in the effort to incorporate proper dairy waste management methods, your company can help minimize its negative impacts on human health and the environment.
Sources of Dairy Waste
From spills and leaks to cheese pressings and brines, the typical main sources of dairy waste are produced at an industrial or farming level.
Dairy Waste on a Farming Level
While there are various types of farm waste, dairy waste is generated by dairy farms and their processes. On a farming level, the dairy waste generated includes:
Spills and Leaks of Products or By-Products
One of the primary sources of dairy waste is spills and leaks that occur during the handling and transportation of dairy products. Accidental spills can contaminate soil, water bodies, and surrounding ecosystems. It is essential for dairy farms and processing facilities to have appropriate procedures in place to quickly address and prevent such incidents.
Residual Milk or Milk Products in Piping and Equipment Before Cleaning
On a farming level, the presence of residual milk or milk products in piping and equipment before cleaning can be a result of spillage or contamination during milking and processing. This waste contributes to the overall waste generated by the dairy industry
Dairy Waste on an Industrial Level
Dairy waste on an industrial level is created from the production of dairy products and includes:
Residual Milk or Milk Products in Piping and Equipment Before Cleaning
After production, residual milk or milk products can linger in the piping and equipment. If these are not properly cleaned, the residues start to break down, grow bacteria, and produce and release harmful substances. To avoid this, you should ensure regular, thorough cleaning and maintenance of your equipment.
Wash Solutions from Equipment and Floors
Cleaning solutions used to sanitize equipment and floors in dairy processing facilities can also contribute to dairy waste. These solutions contain chemicals and organic matter that need proper disposal to prevent environmental contamination. By implementing efficient cleaning practices and using more environmentally friendly products, you can help reduce the volume of waste generated.
Condensate from Evaporation Processes
As milk or other dairy products evaporate, they produce condensate. Condensate contains organic matter and dissolved solids, both of which can be harmful if released into the environment without being properly collected or treated.
Pressings and Brines from Cheese Manufacturers
Cheese making results in pressings and brines, containing high levels of organic matter and salt. These by-products can be challenging to manage because they need to be specially treated to ensure they are properly disposed. If you’re a cheese manufacturer, you should ensure that you have effective waste management systems in place to minimize your environmental impact.
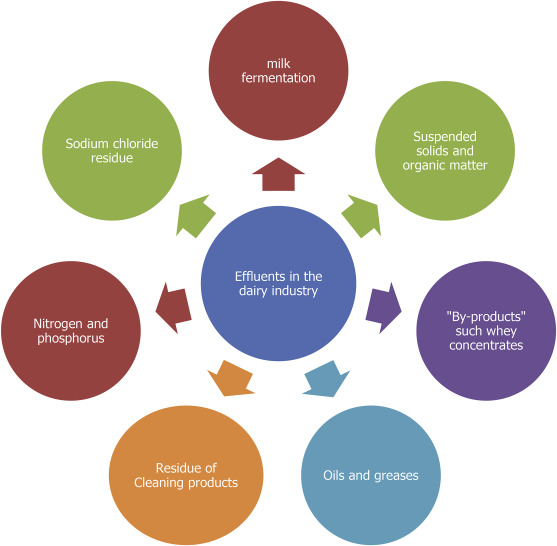
Characteristics of Dairy Wastes
By having a deeper understanding of the characteristics of dairy waste, you’ll be able to devise an effective waste management strategy to prevent further environmental pollution. In this section, we will explore the composition and the physical and chemical attributes that define dairy waste.
Composition
Mainly composed of organic matter, dairy wastes include fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and dissolved solids. Depending on the product, the composition of the waste produced can vary since it has a high organic content.
Physical and Chemical Characteristics
Dairy waste exhibits various physical and chemical characteristics that are necessary to recognize for effective waste management strategies. It can contain:
Physical Characteristics
- A white or yellowish-green color
- An unpleasant smell
- Changes in flow, and temperature
- Soluble organics and suspended solids
- Animal fat
Chemical Characteristics
- Nitrates
- Lipids
- Ammonium
- Sulphates
- Dissolved solids
- D-lactose
- Chlorides
- Phosphates
- Soluble proteins
- Suspended solids
- PH
- Dissolved oxygen
- BOD (biological oxygen demand)
- COD (chemical oxygen demand)
Dairy Waste Management Methods
Now that you understand dairy waste a bit more, you might wonder how you can properly manage it. Fortunately, there are various methods for managing dairy waste – all of which have similar goals – to minimize waste generation, treat and dispose of waste properly, and utilize waste by-products more efficiently.
Common dairy waste management methods include:
Aerobic and Anaerobic Ponds
Aerobic ponds are commonly used to treat dairy waste because they promote the growth of bacteria that helps break down organic matter.
Anaerobic ponds, on the other hand, promote the waste to decompose without oxygen. Both of these types of ponds are used to reduce the organic substances and odors found in dairy waste.
Treatment Ponds and Lagoons
Treatment ponds and lagoons are designed to receive and treat dairy waste through natural processes. By depending on bacteria, sun, and other microorganisms, organic matter starts to break down and contaminants are removed. To ensure the efficiency of these ponds and lagoons, proper maintenance and monitoring should be in place.
Activated Sludge
Activated sludge is a method that uses microorganisms to break down the organic matter found in dairy waste. An aeration tank is used to mix the waste with bacteria and microorganisms where the organic matter is consumed and turned into water, biomass, and carbon dioxide. This process helps reduce the organic load in the waste.
Biological Filtration
In biological filtration, dairy waste goes through a filter that also contains microorganisms which are used to break down the organic matter and remove contaminants. These systems are typically used in combination with other methods to enhance waste management efficiency.
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion is used to break down organic matter without oxygen. anaerobic decomposition is an effective method when the dairy waste that’s being treated has a high organic content. During this process, organic matter is converted into biogas, which can then be used as an energy source, providing an alternative energy option.
Composting
Composting is another sustainable approach that you can use to manage your dairy waste as it can convert it into a usable product. Dairy waste composting uses microorganisms to break down the natural waste to get rid of detrimental organisms and reduce the waste volume. Once the waste is broken down, you’re left with a usable, nutrient-rich compost.
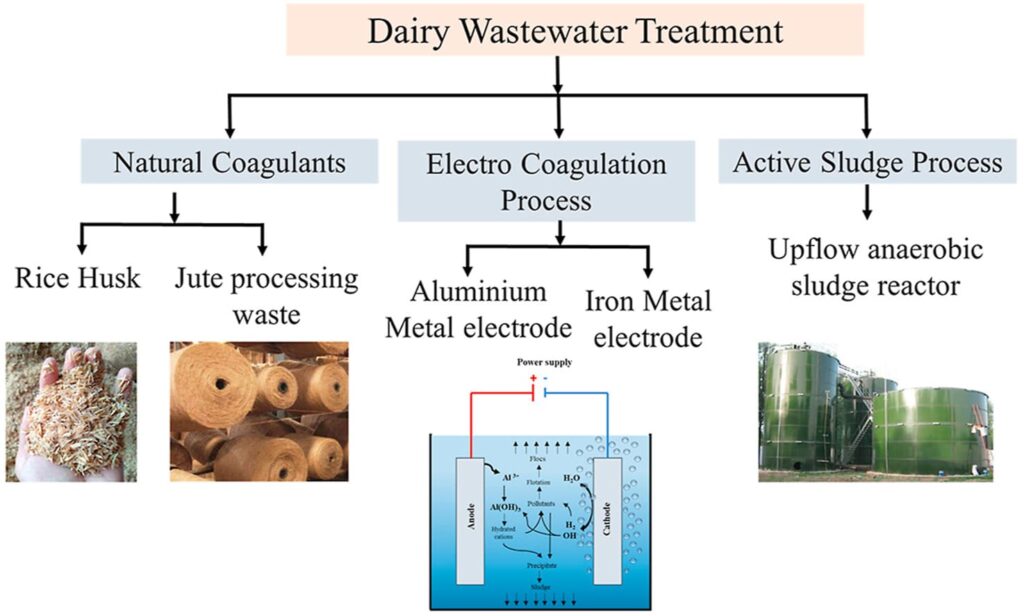
Dairy Waste Treatment Process
The dairy waste treatment process commonly involves multiple stages to help reduce its environmental impact and to make sure it’s properly discarded. The process includes:
- Collection: First, dairy waste is collected from farms, processing plants, and production facilities. The way that the waste is collected must be efficient in order to prevent waste from being released into the environment.
- Storage: After the waste is collected, it needs to be stored in correct containers to ensure there are no spills, leaks, or environmental contamination.
- Treatment: Then, the dairy waste will undergo a variety of treatment methods (as mentioned above) to minimize the amount of contaminants, organic content, and impact. The way the waste is treated will depend on its characteristics and the desired result.
- Transfer: After it’s treated, the waste will then be transferred for advanced handling or disposal
- Utilization: In some cases, dairy waste can be useful. After it’s been treated, by-products can be turned into fertilizer or as a source of energy – as in the anaerobic process. Applying dairy waste productively can reduce its waste volume and provide more value to the industry.
Risks of Improper Dairy Waste Disposal
Like any type of waste, if dairy waste is handled poorly, it can have considerable effects economically and on the environment. Let’s explore the risks of improper dairy waste disposal further:
Environmental Impact
If handled incorrectly, dairy waste can pollute soil, nearby bodies of water, and the air, which can result in the damage of ecosystems. Additionally, because dairy waste has a high organic content, oxygen levels in water can be affected, and subsequently, marine life. On top of this, if pollutants from dairy waste are released into the environment, the ecosystem’s health can be damaged long-term.
Economical Impact
Improper dairy waste management can result in increased energy consumption and costs. Inefficient treatment processes may require more energy input, leading to higher operational expenses for dairy farms and processing facilities. Moreover, the costs associated with pollution management, such as cleaning up contaminated water sources or mitigating environmental damage, can be substantial.
Federal Laws on Dairy Waste
Federal laws and regulations surrounding dairy waste were put in place to address the health and environmental risks associated. In the United States, the federal laws and regulations were established by the Environmental Protection Agency in 1974 and 1975 and are used to govern the management and set the standards for proper treatment and disposal. These guidelines aim to protect water quality and prevent environmental harm by ensuring proper disposal and treatment of dairy waste.
How you incorporate the laws can vary depending on your association with dairy waste. For example, if you are a direct discharger, you need to merge the guidelines with your National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits. If you’re an indirect discharger, you must follow permits or other control mechanisms.
Regardless of your role in the dairy sector, adhering to the rules is vital to protect the environment and ensure the reputation and sustainability of the industry.
Conclusion
Proper dairy waste management and treatment is vital to keep the environment safe. To ensure the dairy industry is held accountable, federal laws and regulations have been put in place.
At Shapiro, we are dedicated to providing effective farm waste management solutions for the dairy sector, we can help you properly implement the right dairy waste solution.
Contact us today to find out how we can assist you in proper dairy waste management and contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Baily Ramsey, an accomplished marketing specialist, brings a unique blend of anthropological insight and marketing finesse to the digital landscape. Specializing in educational content creation, she creates content for various industries, with a particular interest in environmental initiatives.



