Reduce, reuse, recycle. The 3 R’s rule was created to promote environmental conservation and keep food out of landfills, making it an important tool in improving sustainability efforts. But why do we need it?
Unfortunately, food waste has become a global issue, causing environmental, economic, and social implications that require immediate attention. According to food waste facts, about a third of the world’s food is wasted annually, meaning that reducing, reusing, and recycling food waste is more important than ever.
To better understand this complex topic, let’s discuss the 3 R’s in more detail, where we’ll explore the benefits of reducing food waste and how we can reduce, reuse, and recycle to minimize our environmental footprint.
Key Takeaways
- Reduction is the top priority in the 3 R’s rule due to its role in reducing landfill use and minimizing the negative environmental, economic, and social consequences of waste. Food waste reduction efforts align with broader corporate social responsibility goals, help companies comply with new regulations, and offer potential tax deductions.
- Reusing food waste offers a unique opportunity for businesses to create new revenue streams while reaching their sustainability goals. Strategies include upcycling, turning food waste into animal feed, and composting.
- Food waste recycling acts as a sustainable last resort in the 3 R’s rule. There are various strategies that companies can implement to address food waste and recycling, including anerobic digestion, integrating recycling programs into everyday business operations, and partnering with food waste management companies.
What are the 3Rs in Food Waste Management?
The 3 R’s rule is a framework for managing food waste effectively in the food industry. As shown below, reduce, reuse, and recycle are all highly preferred methods in the Food Waste Recovery Hierarchy, with prevention being the most important aspect of reducing landfill use.
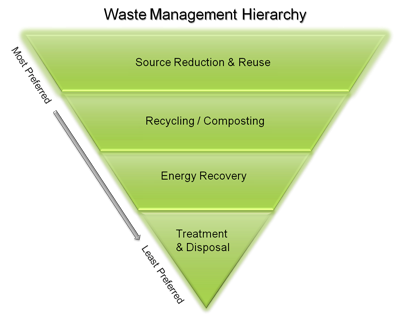
- Reduce refers to minimizing food loss and waste at all stages of the supply chain.
- Reuse focuses on finding alternative uses for materials to prevent waste.
- Recycle involves converting food that would otherwise be disposed of into something new and useful.
The 3 R’s act as a guide for waste management decision-making, providing innovative strategies to keep valuable resources in circulation and reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills.
The Importance of Reducing Food Waste
Reducing food waste at the source should be a top priority for individuals and businesses. As we’ll see below, reducing food waste is key to improving economic and environmental sustainability, promoting a more efficient food system, and helping meet corporate social responsibility goals.
Food Waste Reduction as an Environmental Imperative
The environmental impact of food waste has long-lasting consequences, including the degradation of land, the loss of natural resources, and the production of greenhouse gases. Food waste reduction is a critical aspect of addressing these concerns, helping companies reach their sustainability goals by conserving resources, decreasing methane emissions from landfills, and addressing global warming.
It’s important to note that avoidable and unavoidable food waste require different waste management solutions. While avoidable food waste can be managed through various strategies that prioritize prevention, unavoidable food waste consists of food that was never intended for consumption, meaning it requires a comprehensive food waste recycling strategy.
The Economic Impact of Food Waste
There’s also a large economic impact of food waste that affects individuals and businesses alike. Overall, the UN Food and Agriculture Organization claims that the monetary loss due to food waste around the world amounts to $940 billion annually, illustrating the large financial loss experienced throughout the supply chain.
At the manufacturing level, global food waste on farms amounts to 15.3% of the food produced globally, amounting to a total value of $370 billion. As food moves further down the supply chain, it continues to experience losses, often due to overproduction, poor inventory management, strict aesthetic standards, and consumer behavior.
Food waste throughout the supply chain results in financial loss for everyone involved, from farmers who produce food that is never consumed to consumers who experience increased prices due to inefficiencies in the system. Businesses that want to increase profitability can implement waste management strategies to save money on resources, lower waste disposal costs, take advantage of food waste tax deductions, and create new revenue streams by upcycling surplus food.

Food Waste Reduction and Corporate Social Responsibility
Food waste reduction efforts align with broader corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals, showcasing a company’s commitment to societal and environmental well-being. There are different ways that businesses can implement food waste reduction into their new or existing CSR strategy, such as setting zero-waste targets, improving inventory management to reduce waste throughout the supply chain, or creating a comprehensive upcycling strategy.
In addition to improving sustainability efforts, food waste reduction enhances a company’s reputation among consumers and stakeholders, positioning them as a leader in their industry.
Regulatory Drivers for Reducing Food Waste
Growing regulatory pressures and government initiatives aimed at reducing food waste have become increasingly prevalent in recent years. These measures are motivated by various factors, including environmental, economic, and social concerns.
In the United States, food waste regulations are increasingly being implemented to help reach the U.S.’s goal of cutting food loss and waste in half by the year 2030. The Bill Emerson Good Samaritan Food Donation Act, for instance, encourages businesses and individuals to donate surplus food without being held liable if the food causes harm to the recipients.
There are also several state- and city-wide initiatives that contribute to this movement, such as tax incentives, laws banning the disposal of food scraps in trash or landfills, and various donation efforts. Since policies vary depending on location, businesses must be aware of changing laws to avoid penalties, take advantage of tax incentives, and drive innovation within their industry.
Reusing Food Waste – Turning Waste into Opportunity
Reusing food waste offers a unique opportunity for businesses to create new revenue streams while reaching their sustainability goals. There are multiple ways to reuse food waste, such as converting food waste into energy or getting involved in local initiatives. Keep reading to explore innovative practices that generate value, including food waste upcycling, turning waste into animal feed, and participating in composting initiatives.
Upcycling Food Waste
Food waste upcycling is the process of transforming food items that would otherwise be discarded into higher-value products. There are different strategies that businesses and individuals can use to upcycle ingredients. At the household level, individuals can use old ingredients to create new recipes, such as turning stale bread into breadcrumbs or freezing overripe bananas for smoothies.
Businesses, on the other hand, can implement larger-scale initiatives, such as turning waste into animal feed, using surplus ingredients to create new menu items, and producing biochar.
Food Waste Reuse as Animal Feed
Converting food waste into animal feed presents multiple environmental and economic opportunities, making it a highly effective strategy for reusing food waste. In addition to minimizing landfill use, it acts as a cost-effective alternative to conventional feed, provides a valuable source of nutrition for livestock, and can create a new revenue stream.
Businesses that are interested in exploring this option must follow strict safety protocols to ensure compliance with federal laws, maintain the quality of livestock feed, and safeguard animal health.
Reuse Through Composting Initiatives
Food waste composting is a sustainable approach that converts food waste into valuable compost for agricultural and landscaping applications, working to improve soil fertility, promote higher yields, and reduce the need for water, pesticides, and fertilizers. There are various ways for individuals and businesses to implement or participate in composting initiatives.
At the household level, families can implement at-home composting or get involved in local composting programs. Businesses, on the other hand, can create their own on-site composting or work with a food waste management company to reduce large-scale waste.
Partnerships for Waste Reuse
Partnerships are a critical component of implementing the 3 R’s rule. Partnerships between food businesses and community organizations, such as food banks and agricultural farms, maximize the reuse of surplus food by creating an efficient system of donations and upcycling.
Businesses that collaborate with food waste management companies also have access to tailored solutions, ensure they’re staying up-to-date with changing regulations, and can acquire cost-effective solutions that work for them.

Recycling Food Waste
When reduction and reuse are not possible, food waste recycling acts as a sustainable last resort. This is because food waste and the circular economy are closely connected, as a well-developed system helps keep natural resources in circulation and opens new opportunities for businesses. As we’ll see below, there are various strategies that companies can implement to address food waste and recycling.
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a series of processes in which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The result of this process is two valuable byproducts: biogas, a renewable energy source, and digestate, a nutrient-rich material that can be used as fertilizer.
Overall, the anaerobic digestion of food waste diverts organic waste from landfills, conserves valuable nutrients, provides an eco-friendly alternative for soil amendment, and generates renewable energy. As a result, anaerobic digestion technology has emerged as a sustainable approach to food waste reduction efforts, providing an efficient and environmentally friendly solution.
Integration of Recycling Programs in Business Operations
Businesses that want to integrate food waste recycling programs into their operations should start by conducting a food waste audit. Food waste audits identify how much waste is being generated, what type of waste, and where in the supply chain this waste occurs, allowing businesses to create a comprehensive waste reduction plan based on their specific needs.
To successfully integrate new programs into everyday operations, it’s crucial to provide employee training, have clear processes and safety guidelines, and implement necessary technology to ensure compliance and company-wide participation. Businesses should also monitor their progress over time, which may include evaluating cost savings, environmental impact, and landfill diversion rates.
As mentioned, partnering with a waste management company is a great resource for streamlining new 3R recycling efforts. Aside from creating tailored solutions, they’ll ensure you comply with regulations while minimizing your environmental footprint.
The Role of Packaging in Food Waste Recycling
Packaging is an important aspect of the 3 R’s because of its ability to protect food and extend the shelf life of products. Packaging design and materials can also help facilitate food waste recycling, potentially reducing contamination and helping companies reach their sustainability goals.
Biodegradable packaging is a great example of how innovative design and materials can increase the efficiency of recycling processes. Packaging that naturally decomposes not only reduces the environmental impact of plastic packaging but also simplifies the sorting process at recycling facilities, contributing to a circular economy.
Technologies and Innovations Supporting the 3 R’s
Food waste technology has emerged as an effective tool for tracking, managing, and reducing waste. AI and IoT solutions are especially important in streamlining processes due to their real-time monitoring capabilities, ability to improve transportation and storage logistics, and their role in enabling data-driven decisions.
That said, one of the most important features of AI in food waste management is its ability to improve inventory management. By leveraging AI’s predictive analytics, businesses can get valuable insights into future trends and events, allowing them to reduce overproduction and waste.
Conclusion
Businesses that want to reduce, reuse, and recycle food waste must implement company-wide initiatives to improve their sustainability efforts. If you’re interested in learning more about how you can apply the 3 R’s rule to your business operations, we recommend working with a food waste management company to find a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution.
At Shapiro, we provide tailored solutions that cater to your specific business needs. By implementing innovative technology and techniques, we’ll help you collect, transport, treat, and recycle waste without disrupting your everyday business operations.
To learn more about our services, contact us today.
Baily Ramsey, an accomplished marketing specialist, brings a unique blend of anthropological insight and marketing finesse to the digital landscape. Specializing in educational content creation, she creates content for various industries, with a particular interest in environmental initiatives.