Did you know that around 1.3 billion tons (or 17%) of the total global food production is wasted? That’s an overwhelming number to wrap your head around. Such an enormous amount of food waste has a negative impact on the environment and your bottom line as well.
Luckily, in today’s world, advanced technologies can help you minimize food waste in an efficient and timely manner.
But how can technology reduce food waste?
The solutions vary from applying techniques like anaerobic digestion, using advanced software, and installing devices that track fill levels.
In this article we will talk all about food waste technology. It’s one of the most important branches among different emerging tech advancements in the field of food science.
What is Food Waste Technology and Why it Matters
Food waste technology is an innovative and rapidly evolving branch of food science that uses different technological advancements to manage food waste.
This branch derives from the broader food technology field, which deals with quality control, food manufacturing, and processing.
On the other hand, food waste technology deals with things like:
- Collection: Advanced sensor-based systems and devices can now track food waste generation, providing precise data and analysis. This helps companies create more accurate resource allocation and make better decisions.
- Treatment and recycling: Technology is used to repurpose food waste into useful resources. For example, advanced composting processes can convert food waste into biofuel or compost. Such sustainable techniques can significantly reduce the environmental impact of food waste.
- Prevention: Predicting when and where food waste will occur is a powerful way to optimize food resources and minimize waste before it’s too late. To do that, companies use artificial intelligence, data analytics, and other advanced technologies to understand patterns and predict food waste occurrences.
Which Advancement in Technology Has Helped Cut Down on Waste
While there are many emerging food waste management technologies, it could be hard to understand what solution would be most suitable for your business needs.
Here are a few great software solutions and technologies that have the most potential.
Food Waste Management Software and Apps
These food waste apps and platforms can help you transform the way you manage your food waste as a business establishment:
- ISB Global: This food waste management software solution helps businesses track, monitor, and analyze food waste efficiently. The software enables organizations to identify areas of improvement and set food waste reduction goals and strategies. As ISB Global can integrate with your existing systems and provide useful reporting and analytics features, it is a powerful tool you can use to minimize food waste.
- Winnow Solutions: The Winnow AI-powered system helps businesses in the hospitality and foodservice industry collect and analyze food waste data. This restaurant food waste technology solution allows organizations to pinpoint exactly when and where waste occurs so they can make better decisions.
- Leanpath: The Leanpath platform is a food waste management solution targeting commercial kitchens and foodservice organizations. Through its advanced food waste tracking and measurement features, kitchens can make better purchasing and allocation decisions while minimizing food waste throughout the supply chain.
- Full Harvest: The Full Harvest food waste management platform acts as an online marketplace where farms and commercial produce buyers can connect. This way, farmers and growers can reduce waste by selling their surplus fruits and vegetables that would otherwise go to waste. At the same time, businesses get access to good quality food at reduced prices.
- Wasteless: The Wasteless software helps retailers adopt AI-powered dynamic pricing strategies to minimize food waste. The solution uses real-time data to ensure supermarkets and online grocery stores capture the full value of their perishable produce and optimize sales.
Food Waste Tracking Technology
Food waste tracking technology helps collect and analyze food waste data. This allows you to monitor, track, and evaluate food waste generation patterns. The data gives valuable insights into key trends, which helps to come up with strategies to minimize food waste.
An advanced tracking system also gives access to real-time data on major food waste inefficiencies. For example, one such technology is bin tracking, which helps track waste containers. This system also allows you to:
- Monitor your waste containers and get insights into your daily waste operations.
- Optimize collection schedules.
- Reduce unnecessary pickups and associated transportation emissions.
- Identify waste hotspots and come up with strategies to reduce food waste in these areas (such as portion control, better inventory management, etc.)
Food Waste Treatment Technology
Food waste treatment technologies transform organic waste into other resources, minimizing their negative environmental impact.
Let’s explore two specific food waste-to-water technologies:
- Food waste liquefiers: Liquefiers are advanced food waste treatment systems that turn organic waste into water, reducing the volume of food waste. This food waste recycling technology is used by big commercial establishments, such as restaurants and hotels. The process involves blending the food waste into a homogenous mixture. The mixture is then broken down into liquid form (through mechanical turning or agitation). The end result can be processed by wastewater treatment systems or discharged into the sewer system.
- Hydrothermal treatment: This process involves treating organic waste in high-temperature (typically above 100°C) and high-pressure conditions. This breaks down the food waste into simpler components, releasing nutrients and energy. These can be further processed using anaerobic digestion to produce biogas or compost.
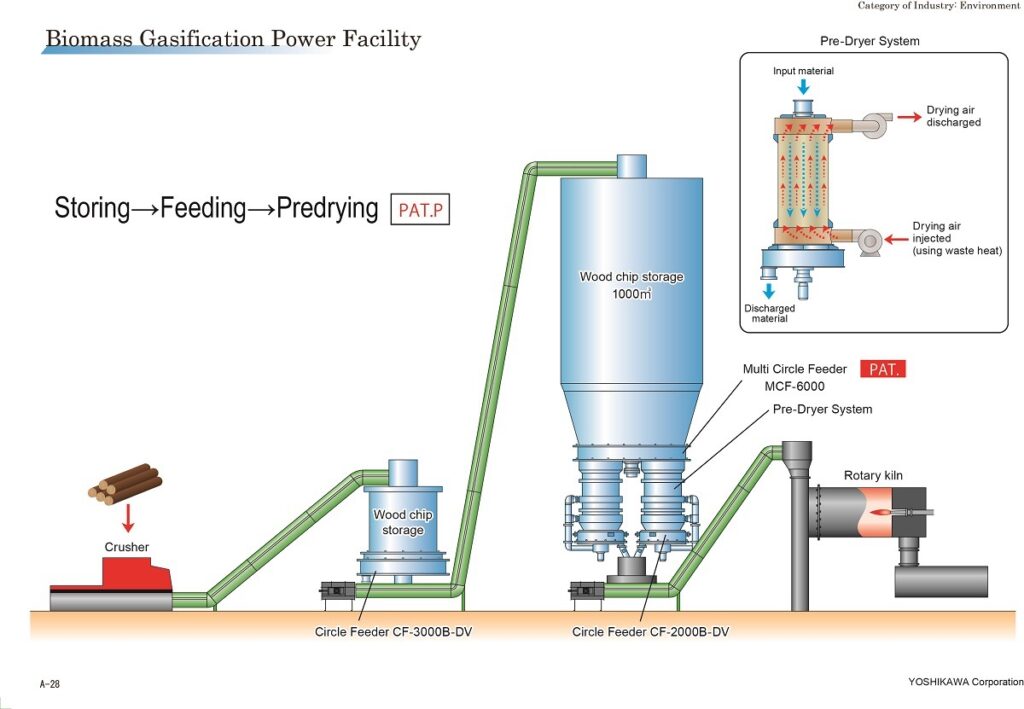
Smart and Emerging Food Waste Management Technologies
The whole smart waste management market is predicted to grow by 15.1%, from $1,683 million in 2019 to $4,103.6 in 2027. So, it’s no surprise that the number of waste management software solutions and technologies is constantly increasing.
Here are some of the latest and most advanced food waste management technologies:
- Smart bin sensors: Waste bins can now be enhanced with smart IoT sensors that monitor fill levels, orientation, and temperature. All sensors are connected via the IoT network and provide advanced 3D topology maps of all your bins, helping you streamline your waste management efforts. This can also help you plan your trash pickup routes and substantially reduce fuel consumption.
- Plasma gasification: This food waste to energy technology uses plasma to heat waste at high temperatures. The main byproduct of this process is hydrogen gas. The gas is then used in hydrogen fuel cells, powering different green energy processes.
- AI-powered supply chain management: Managing food resources can be tough, especially in large-scale organizations. Predicting future supply and demand trends, accurate resource allocation, and tracking expiration dates while maintaining all food safety regulations can now be optimized using AI-based software.
- Solar-powered trash compactors: These trash compactors can hold up to 5 times more waste than regular non-compacting bins, reducing the waste collection frequency by up to 80%. This enables faster and more efficient waste management in both rural and urban locations.
- Garbage truck advances: Smarter garbage truck mechanisms can now predict fill levels so waste collection trips can be streamlined and optimized. But how does this work exactly? The mechanism can measure the weight of waste containers and store this data. Based on that, companies can predict future fill levels, understanding how many trucks to send at a time.
Examples of Food Waste Technology Real-Life Applications
Food waste technology is paving the way to a more sustainable future. For example, it has already changed the way food recycling is done.
The two main food recycling processes are:
- Composting: This converts organic waste into nutrient-rich compost that improves soil health and yields.
- Anaerobic digestion: This helps turn organic waste into biogas (which can be used as a source of renewable energy) and biofertilizers (that can enhance soil quality).
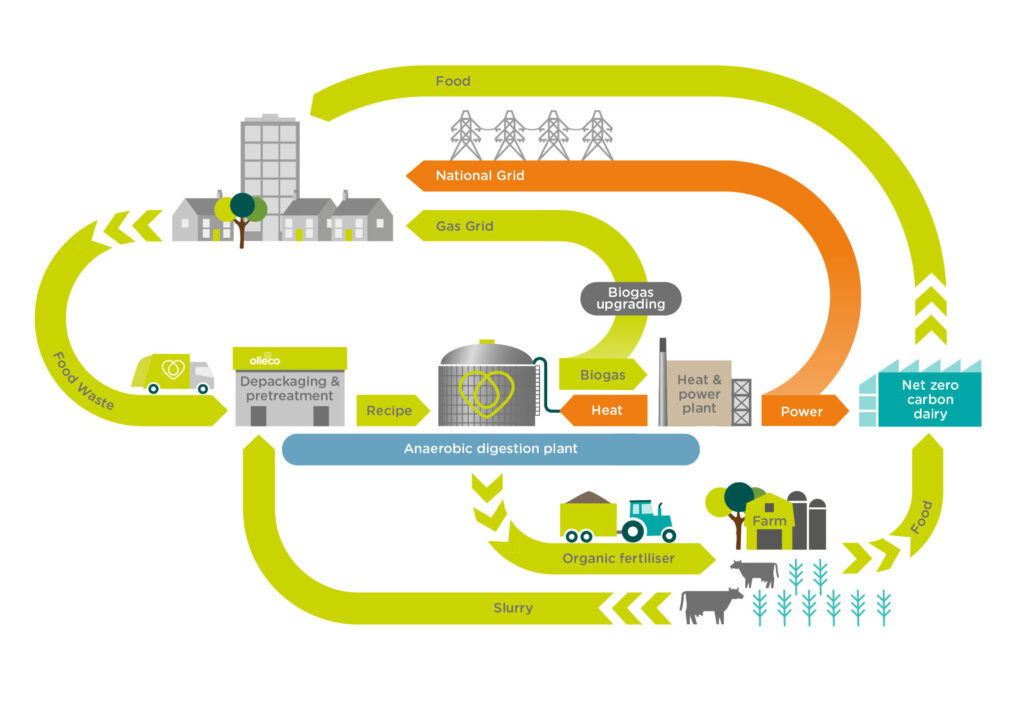
Now, let’s look at the specific technology used in these two food waste recycling applications.
Food Waste Composting Technology
Composting can be done in a few different ways, including:
- Mechanical composting: This process uses different machines (shredders, mixers, and grinders) that break down the waste into small particles. This method speeds up the natural decomposing process and ensures better aeration and mixing of the compounds.
- Automatic turning in-vessel composting: This technology utilizes closed vessels equipped with turning mechanisms that rotate the food waste periodically. This way, the compost is mixed and aerated well. At the same time, the enclosed system provides optimal conditions for microbial activity, accelerating the decomposition process.
- Electrical home composting: Such composters allow users to compost in their own households. You just need to load the food remains in the composter, and it will automatically create an optimal, controlled decomposition environment.
- Forced aerated windrow composting: This involves creating long narrow piles of compostable waste. This allows optimal airflow, temperature, and moisture levels, making it an ideal solution for large business composting facilities.
Food Waste Digestion Technology
The first record of anaerobic digestion is from 10 BC when biogas was used to heat bath water. However, the first anaerobic digestion machine was built much later, in 1859.
But how does anaerobic digestion work exactly?
The process uses fermentation to break down organic matter and it usually takes place in special anaerobic digester systems.
Here’s a breakdown of the main steps:
- Loading: The organic waste is crushed into a homogenized mixture that’s loaded into the anaerobic digester vessel.
- Fermentation: The mixture is then heated up to a temperature of 37°C -38°C. In the span of around 20 days the biomass goes through different chemical transformations and produces biogas (a mix of methane and carbon dioxide) as a byproduct.
- Biogas applications: The methane can be then extracted and used as a natural gas or transportation fuel.
- Removal: The leftover material can be used as a fertilizer for crops.
Today, there are about 60 anaerobic digestion facilities in the US alone. They’re split into two main categories:
- Dedicated facilities: Such facilities are located right at the production plant and process only their own waste.
- Merchant facilities: These facilities accept waste from different manufacturing and processing plants and can handle large amounts of organic waste.
How Can Technology Reduce Food Waste and Why Adopt it
The food waste technology field has seen great progress in recent years. Today, there are more new and innovative ways of dealing with food waste collection, processing, and recycling.
These are slowly substituting the old methods in the industry, which are more costly and detrimental to the environment.
Adopting advanced food waste technology into your business operations can have a positive effect on your bottom line, productivity, and success. At the same time, it also helps the environment and drives sustainability.
Ready to adopt some of the most advanced food waste technologies into your daily business operations but not sure where to start? At Shapiro, we have vast experience in the field and partners all over the US who can cover all the technicalities of the complex food waste recycling and upcycling process
Contact us today to learn more and adopt some of the latest food waste technologies.
Baily Ramsey, an accomplished marketing specialist, brings a unique blend of anthropological insight and marketing finesse to the digital landscape. Specializing in educational content creation, she creates content for various industries, with a particular interest in environmental initiatives.



